How to operate a drone? It’s a question many ask, intrigued by the possibilities of aerial photography and exploration. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety procedures to mastering advanced flight techniques and understanding legal regulations. We’ll cover everything you need to know to safely and effectively pilot your drone, capturing stunning aerial footage along the way.
Prepare to unlock the skies!
We’ll navigate the essential steps, from understanding your drone’s controls and navigating its various flight modes to mastering camera settings for breathtaking visuals. We’ll also explore crucial safety protocols, legal considerations, and maintenance tips to ensure the longevity of your equipment. This guide provides a clear path to confidently taking to the skies.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring a safe and successful drone flight. Overlooking even minor details can lead to accidents or equipment damage. This section details a comprehensive checklist and safe launch procedure.
Pre-Flight Inspection Importance
Pre-flight checks mitigate risks associated with malfunctioning equipment. A damaged propeller, low battery, or weak GPS signal can cause crashes, loss of control, or even injury. Regular inspections become a habit that significantly reduces potential hazards.
Comprehensive Pre-Flight Checklist
The following checklist covers essential pre-flight steps. Always refer to your drone’s specific manual for model-specific instructions.
| Item | Check | Status (Pass/Fail) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Check battery indicator and voltage | Pass/Fail | Ensure sufficient charge for planned flight time, consider extra battery |
| Propeller Inspection | Examine propellers for cracks, damage, or loose attachments | Pass/Fail | Replace damaged propellers immediately |
| GPS Signal | Verify GPS signal strength and satellite lock | Pass/Fail | Ensure sufficient satellites are acquired for stable flight |
| Gimbal Calibration | Check gimbal alignment and functionality | Pass/Fail | Recalibrate if necessary, refer to drone manual |
| Sensor Check (if applicable) | Verify functionality of obstacle avoidance sensors | Pass/Fail | Clean sensors if necessary |
| Flight Controller Status | Check for any error messages on the controller | Pass/Fail | Address any errors before flight |
| Environment Check | Assess wind conditions, obstacles, and airspace restrictions | Pass/Fail | Postpone flight in unfavorable conditions |
Safe Drone Launch Procedure
- Power on the remote controller first, followed by the drone.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition (indicated by lights or app).
- Calibrate the compass if prompted.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration or check as per manufacturer’s instructions.
- Slowly lift the drone a few feet to verify stability and control.
- Begin your flight operations.
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains basic controls, different control schemes, and flight modes.
Basic Drone Controls
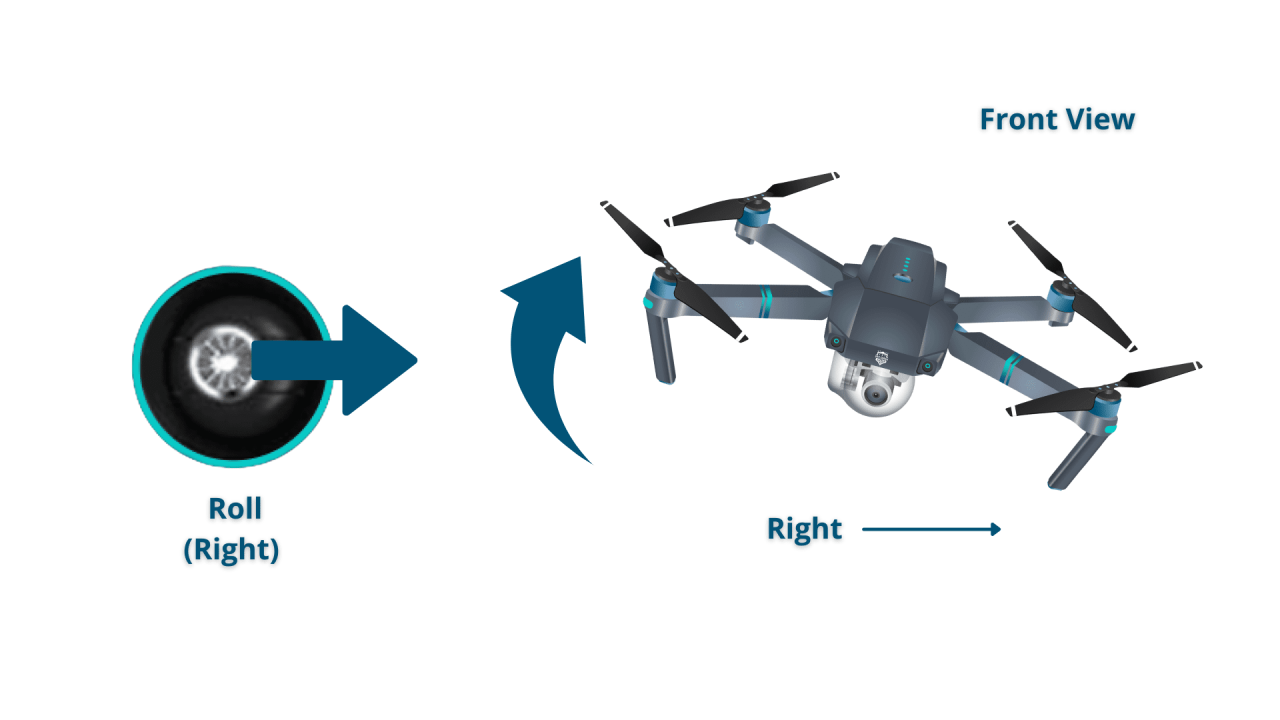
Most drones utilize two control sticks and several buttons. One stick controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right), while the other controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude). Buttons typically control functions like camera operation, return-to-home, and emergency stops.
Control Schemes: Mode 1 vs. Mode 2

Mode 1 and Mode 2 refer to the stick assignments. In Mode 1, the left stick controls throttle and yaw, while the right stick controls pitch and roll. Mode 2 reverses these assignments. The choice depends on personal preference and prior experience with RC vehicles.
Flight Modes, How to operate a drone

Many drones offer different flight modes to adjust responsiveness and stability. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for faster, more agile maneuvers. GPS mode utilizes satellite data for precise positioning and return-to-home functionality.
| Control | Function |
|---|---|
| Left Stick (Vertical) | Throttle (Altitude) |
| Left Stick (Horizontal) | Yaw (Rotation) |
| Right Stick (Vertical) | Pitch (Forward/Backward) |
| Right Stick (Horizontal) | Roll (Left/Right) |
| Button 1 | Camera Shutter/Record |
| Button 2 | Return-to-Home |
| Button 3 | Emergency Stop |
Drone Navigation Using Waypoints
Waypoints allow for pre-programmed flight paths. By setting waypoints in a flight planning app, the drone autonomously navigates between designated points, enabling complex shots and reducing pilot workload. This is particularly useful for creating cinematic aerial footage.
Understanding Drone Camera and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and composition techniques. This section explores camera settings, image capture processes, and composition tips.
Drone Camera Settings
Drone cameras offer various settings to adjust image quality and style. Resolution determines image size, ISO controls sensitivity to light (affecting noise), shutter speed affects motion blur, and aperture affects depth of field. Understanding these settings is crucial for optimizing image quality in different lighting conditions.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
To capture high-quality aerial photos and videos, consider factors such as lighting, composition, and camera settings. Shoot during the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for soft, warm light. Use appropriate ISO and shutter speed settings to avoid noise and motion blur. Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives to find the best composition.
Tips for Compelling Aerial Shots
Aerial photography benefits from careful composition. Use leading lines to guide the viewer’s eye, apply the rule of thirds for balanced framing, and consider the perspective and angle to enhance visual interest. Plan your shots and use different camera angles to tell a compelling visual story.
| Setting | Effect on Image Quality |
|---|---|
| Resolution | Higher resolution means larger file size and more detail |
| ISO | Higher ISO increases sensitivity but introduces noise |
| Shutter Speed | Faster shutter speed freezes motion, slower shutter speed creates motion blur |
| Aperture | Controls depth of field; wider aperture creates shallow depth of field |
Creating a Timelapse Video
- Plan your shot and select appropriate camera settings.
- Use intervalometer or app function to set capture intervals.
- Ensure stable positioning using GPS or other stabilization methods.
- Capture a sequence of images over a desired time period.
- Use video editing software to combine images into a timelapse video.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your drone and prevents unexpected issues. This section covers common problems, cleaning procedures, and battery care.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Common issues include low battery warnings, GPS signal loss, propeller damage, and camera malfunctions. Addressing these issues promptly prevents escalation and potential accidents. Always refer to the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide for specific solutions.
Cleaning and Maintaining Drone Components
Regularly clean the drone’s body, propellers, and camera lens with a soft cloth and appropriate cleaning solution. Inspect for any loose parts or damage and address them immediately. Store the drone in a dry, safe place to prevent damage from dust or moisture.
Extending Drone Battery Lifespan
- Avoid fully discharging or overcharging batteries.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Use a proper charger and follow manufacturer’s instructions.
- Avoid extreme temperatures.
Recommended Maintenance Tasks
- Daily: Inspect propellers and body for damage.
- Weekly: Clean drone body and propellers.
- Monthly: Inspect and clean camera lens and sensors.
- Quarterly: Perform a more thorough inspection of all components.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Low battery warnings indicate the need for recharging. GPS signal loss may be due to interference or poor satellite visibility. Consult your drone’s manual for detailed troubleshooting steps.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From pre-flight checks to mastering maneuvers, this guide covers everything you need to know to operate a drone responsibly and safely.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local regulations. This section highlights the importance of legal compliance and provides resources for finding relevant information.
Relevant Regulations and Laws
Drone regulations vary by region. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules and laws governing drone operation in your area. These regulations often cover airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
In some regions, operating a drone requires permits or licenses, especially for commercial use or specific flight operations. Check with your local aviation authority to determine any necessary permits or licenses before flying.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Certain areas have airspace restrictions, such as airports, military bases, and national parks. These areas are designated as no-fly zones to ensure safety and security. Using flight planning software or apps helps identify and avoid restricted airspace.
Resources for Drone Regulations
- Your country’s national aviation authority website.
- Local government websites.
- Drone industry associations.
Examples of Restricted Drone Operation
Flying near airports, power lines, or crowded areas is generally restricted. Flying at night or in poor weather conditions may also be prohibited, depending on local regulations. Always prioritize safety and comply with all applicable laws.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced maneuvers and flight techniques to enhance your drone piloting skills and capture more dynamic footage.
Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, are possible with certain drone models. These maneuvers require practice and a thorough understanding of drone controls. Always practice in a safe, open area and prioritize safety.
Flight Techniques for Various Shooting Scenarios
Tracking moving subjects requires smooth and precise control. Different flight techniques are needed for various shooting scenarios, such as capturing landscape shots, tracking moving vehicles, or filming dynamic action scenes. Practice is key to mastering these techniques.
Planning Complex Drone Flights
Flight planning software allows for pre-programming complex flight paths with waypoints, camera angles, and other parameters. This enables intricate shots and reduces manual control during filming, resulting in smoother and more professional footage.
Achieving Smooth and Stable Aerial Footage
Smooth and stable footage is crucial for professional-looking results. Use appropriate flight modes, maintain a steady hand, and consider using additional stabilization equipment, such as gimbals or image stabilization software.
Using Different Camera Angles
Experimenting with various camera angles adds visual interest to your footage. Low angles can create a sense of scale and grandeur, while high angles provide a broader perspective. Using a variety of angles keeps your viewers engaged and adds depth to your story.
Drone Photography and Videography Composition
Effective composition is key to creating visually appealing aerial content. This section discusses the principles of composition and how to apply them to drone photography and videography.
Principles of Aerial Composition
The rule of thirds, leading lines, and the use of negative space are all essential compositional elements in aerial photography and videography. These principles create visual balance and guide the viewer’s eye through the scene.
Effective Composition Techniques
Imagine a sweeping shot of a winding river, with the river forming a strong leading line towards a distant mountain range, showcasing the vastness of the landscape. This uses leading lines to draw the viewer’s eye and create a sense of depth. Alternatively, a shot of a lone tree in a field, positioned at one of the rule of thirds intersections, provides a balanced and visually pleasing composition.
Leading Lines, Rule of Thirds, and Other Elements
Leading lines, such as roads or rivers, naturally draw the viewer’s eye through the image. The rule of thirds suggests placing key elements off-center for a more dynamic composition. Negative space, or empty areas in the frame, can enhance the impact of the main subject.
Capturing Dynamic and Engaging Aerial Footage
Dynamic footage keeps the viewer engaged. Use smooth camera movements, varied angles, and creative compositions to create a visually stimulating experience. Consider using slow pans, tilts, or zooms to enhance the storytelling aspect of your footage.
| Camera Angle | Intended Effect |
|---|---|
| High Angle | Provides a broad overview and sense of scale. |
| Low Angle | Emphasizes height and grandeur; creates a sense of power. |
| Dutch Angle | Creates a feeling of unease or disorientation. |
| Bird’s-eye View | Offers a unique perspective, revealing patterns and relationships. |
Mastering drone operation is a journey, not a destination. This guide has equipped you with the foundational knowledge and practical skills to safely and effectively pilot your drone. Remember, continuous practice and a commitment to safety are key to unlocking the full potential of this exciting technology. So, take to the skies responsibly, capture breathtaking moments, and enjoy the incredible perspective only a drone can provide.
Happy flying!
Helpful Answers: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home functionality, and beginner-friendly flight modes.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies depending on the model and usage. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge. Always carry extra batteries.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If GPS is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its starting point. However, always maintain visual contact with your drone.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safety protocols. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical exercises, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and become proficient in piloting your own drone. Remember, responsible drone operation is paramount for both safety and legal compliance.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures.
Can I fly my drone anywhere?
No. Drone operation is subject to various restrictions, including airspace limitations, no-fly zones near airports, and privacy concerns. Always check local regulations before flying.